
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Electronic Information Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Precision Manufacturing Technology of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Shenzhen Technology University, Shenzhen 518118, China
Swept source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT) is a new noninvasive technique for assessing tissue. Although it has advantages, such as being label-free, noninvasive, and with high resolution, it also has drawbacks: there has been no in-depth research into identifying the driving of swept source. Based on preliminary research, we demonstrate a novel driving modulation method of a fiber Fabry–Perot tunable filter ranging phase adjustable as a tool for making bandwidth compensation of a swept laser source. This novel method is analyzed in detail; a swept laser source with a sweep rate of 100.5 kHz over a range of 152.25 nm and at a center wavelength of 1335.45 nm is demonstrated.
swept laser source optical design techniques ring lasers laser applications Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(1): 011407
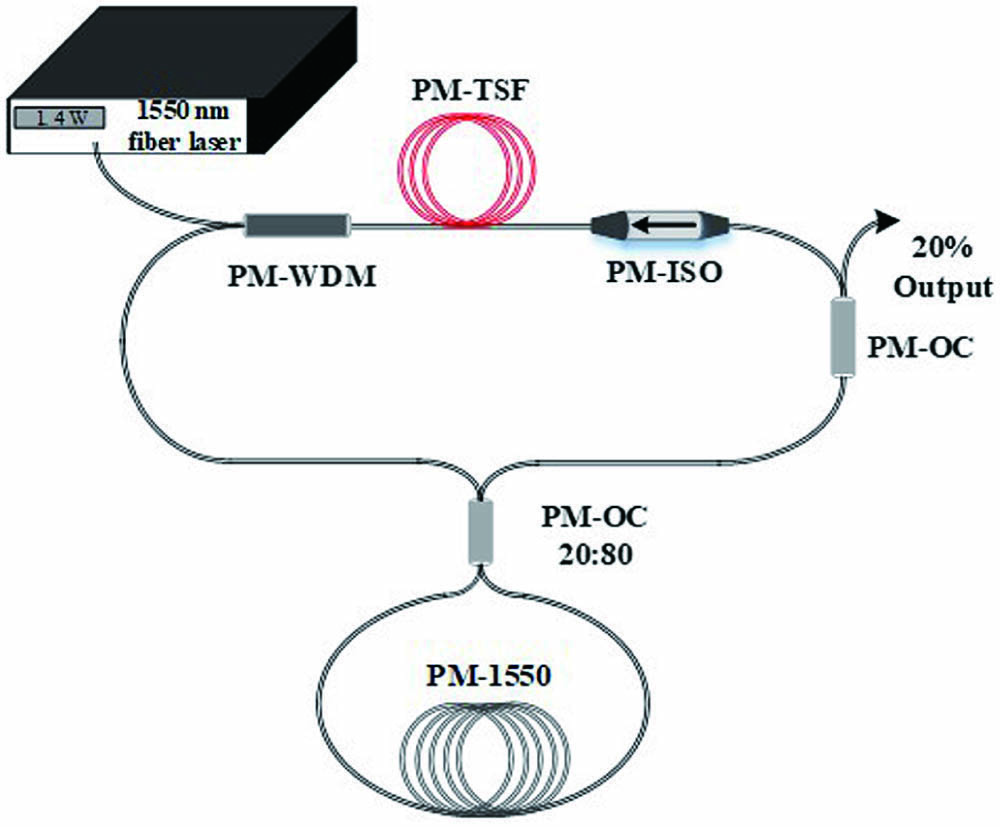
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Precision Manufacturing Technology of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Sino-German College of Intelligent Manufacturing, Shenzhen Technology University, Shenzhen 518118, China
2 College of Electronics and Information Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
A stable noise-like (NL) mode-locked Tm-doped fiber laser (TDFL) relying on a nonlinear optical loop mirror (NOLM) was experimentally presented. Different from the previous NL mode-locked TDFL with NOLM, the entire polarization-maintaining (PM) fiber construction was utilized in our laser cavity, which makes the oscillator have a better resistance to environmental perturbations. The robust TDFL can deliver stable bound-state NL pulses with a pulse envelope tunable from ~14.1 ns to ~23.6 ns and maximum pulse energy of ~40.3 nJ at a repetition rate of ~980.6 kHz. Meanwhile, the all-PM fiber laser shows good power stability (less than ~0.7%) and repeatability.
noise-like pulse all-polarization-maintaining fiber nonlinear loop mirror Tm-doped fiber laser Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(9): 091402
1 深圳大学信息工程学院, 广东 深圳 518060
2 深圳大学物理与光电工程学院深圳市激光工程重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
3 深圳技术大学, 广东 深圳 518118
4 山东大学晶体材料国家重点实验室和晶体材料研究所, 山东 济宁 250100
5 深圳市大族激光科技股份有限公司, 广东 深圳 518057
首次搭建了基于ZnWO4/Nd∶YAG的一阶斯托克斯拉曼激光器,并研究了其在不同重复频率与不同输出耦合镜下的输出特性。采用ZnWO4晶体作为拉曼晶体,二极管泵浦Nd∶YAG晶体产生基频光,实现了波长为1177.6 nm的一阶斯托克斯激光输出。当输出耦合镜的透过率为35%,泵浦功率为22.1 W,重复频率9 kHz时,在1177.6 nm处获得了最大平均输出功率,为886 mW,对应的最短脉宽为2.2 ns,峰值功率为43.9 kW。
激光器 固体激光器 拉曼 ZnWO4晶体

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Precision Manufacturing Technology of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Shenzhen Technology University, Shenzhen 518118, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and System of Ministry of Education, College of Optoelectronic Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
3 Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Laser Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
4 Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Precision Manufacturing Technology of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Shenzhen Technology University, Shenzhen 518118, China
We report on mode-locked thulium-doped fiber lasers with high-energy nanosecond pulses, relying on the transmission in a semiconductor saturable absorber (SESA) and a carbon nanotube (CNTs-PVA) film separately. A section of an SMF–MMF–SMF structure multimode interferometer with a transmission peak wavelength of ~2003 nm was used as a wavelength selector to fix the laser wavelength. When the SESA acted as a saturable absorber (SA), the mode-locked fiber laser had a maximum output power of ~461 mW with a pulse energy of ~0.14 μJ and a pulse duration of ~9.14 ns. In a CNT-film-based mode-locked fiber laser, stable mode-locked pulses with the maximum output power of ~46 mW, pulse energy of ~26.8 nJ and pulse duration of ~9.3 ns were obtained. To the best of our knowledge, our experiments demonstrated the first 2 μm region ‘real’ SA-based dissipative soliton resonance with the highest mode-locked pulse energy from a ‘real’ SA-based all-fiberized resonator.
high pulse energy mode-locking nanosecond pulse Tm-doped fiber laser High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2020, 8(2): 02000e14
1 深圳大学电子与信息工程学院, 广东 深圳 518060
2 深圳大学深圳市激光工程重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
3 山东大学晶体材料国家重点实验室, 山东 济南 250100
4 深圳技术大学, 广东 深圳 518118
5 大族激光科技股份有限公司, 广东 深圳 518057
为研究ZnWO4晶体的二阶拉曼性质,搭建了基于ZnWO4晶体的二阶拉曼激光器,实现了重复频率为9 kHz的670 mW的1318.3 nm的二阶斯托克斯激光输出,对应的脉宽为3.294 ns,光光转换率为4.7%,峰值功率达到22.6 kW。实验结果表明,ZnWO4晶体具有良好的性能,能够实现二阶拉曼激光输出。
固体激光器 拉曼激光器 ZnWO4晶体
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Laser Engineering, Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Precision Manufacturing Technology of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro/Nano Optomechatronics Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Sino-German College of Intelligent Manufacturing, Shenzhen Technology University, Shenzhen 518118, China
3 Key Laboratory of ATR National Defense Science and Technology, College of Information Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
We demonstrate, for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, an all-fiber figure-of-9 double-clad Tm-doped fiber laser operating in the dissipative soliton resonance (DSR) regime. Stable mode-locked rectangular pulses are obtained by using the nonlinear amplifying loop mirror (NALM) technique. A long spool of high-nonlinearity fiber (HNLF) and a segment of SMF-28 fiber are used to enhance the nonlinearity of the NALM loop and to obtain a large all-anomalous regime. Output power and pulse energy are further boosted by using a three-stage master oscillator power amplifier (MOPA) system. At the maximum pump power, average output power of up to 104.3 W with record pulse energy of 0.33 mJ is achieved with a 2 μm DSR-based MOPA system.
Photonics Research
2019, 7(5): 05000513

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Laser Engineering, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Micro/Nano Optomechatronics Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 College of Information Engineering, ATR National Defence S&T Key Laboratory, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
3 Institute of Applied Physics & Materials Engineering, Faculty of Science and Technology, University of Macau, Macau, China
Short pulsed fiber lasers have been widely made using single-walled carbon nanotubes as a saturable absorber (SA). However, most of the currently used devices can only operate in one determined operation state with an unchangeable modulation SA depth in the cavity, which significantly limits their application in photonic devices. In this paper, well-aligned carbon nanotube arrays are synthesized using zeolite AlPO4-5 as a template, which features anisotropic optical absorption. The linear optical absorption of the as-synthesized carbon nanotube arrays can easily be tuned by adjusting a polarization controller, thus providing a tunable modulation depth for the carbon nanotube SA. By exploiting this SA in an erbium-doped fiber laser cavity, both Q-switched and mode-locked pulsed lasers are achieved by simply adjusting a polarization controller under a fixed pump power of 330 mW. In addition, the repetition rate of the Q-switching and pulse duration of the mode-locking can be tuned according to the variation of modulation depth. Moreover, soliton molecules can be obtained when the modulation depth of the SA is 4.5%.
Photonics Research
2018, 6(11): 11000996
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Information Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060
2 Intelligent Information Processing Laboratory, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060
In landmark-based image registration, estimating the landmark correspondence plays an important role. In this letter, a novel landmark correspondence estimation technique using mean shift algorithm is proposed. Image corner points are detected as landmarks and mean shift iterations are adopted to find the most probable corresponding point positions in two images. Mutual information between intensity of two local regions is computed to eliminate mis-matching points. Multi-level estimation (MLE) technique is proposed to improve the stability of corresponding estimation. Experiments show that the precision in location of correspondence landmarks is exact. The proposed technique is shown to be feasible and rapid in the experiments of various mono-modal medical images.
100.6950 Tomographic image processing 100.0100 Image processing Chinese Optics Letters
2008, 6(12): 950
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Information Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060
Multisensor image fusion could improve system performances such as detection, tracking, and identification greatly. In this paper, a long distance target detection approach is presented based on multisensor image features fusion. This method extracts two different features from visual and infrared (IR) image sequences respectively to detect regions of motion information content. Temporal change feature is extracted from the visual image sequence using temporal decomposition based on wavelet, which reflects the dynamical content variation at a pixel at any time. And correlation features between local regions are extracted from IR image sequence to distinguish regions with potential moving targets. All these features are merged into a multi-dimensional space and the support vector machine is trained to select regions that have the potential target at each pixel location. The method is robust and feasible to detect long distance targets in clutter background scene.
目标检测 图像融合 分类 100.5010 Pattern recognition 100.2960 Image analysis 100.2000 Digital image processing Chinese Optics Letters
2007, 5(7): 400
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Information Engineering, Shenzhen University
2 Modern Education Technology and Information Center, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060
Mutual information (MI) based image registration has been found to be quite effective in many medical image applications. However, standard MI hampers the convergence of registration transformation parameters since it contains local maxima. In this paper, a novel registration method is proposed. At first, MI based on edge width matching is computed to avoid great change of joint probability distribution and get less local maxima. Particle swarm optimization (PSO), which combines local search methods with global ones balancing exploration and exploitation, is done to search the optimal registration parameter. PSO has less computational complexity as its complex behavior follows only a few simple rules. It could avoid local maxima and reach global optimal results. This method is applicable to a variety of multimodal images, and suitable to different interpolation methods. Theoretical analysis and experiments show that this method is effective and accurate to register multimodal medical images.
100.0100 image processing 350.2660 fusion Chinese Optics Letters
2005, 3(9): 09510





